What If A Mutation Occurred In The Human Insulin Gene And The First Triplet Was Changed To Ccg
Recognize the touch on of Dna mutations
In this outcome, we'll learn just what mutations are and how they're frequently connected to our DNA.
Learning Objectives
- Understand what a mutation is and how one generally occurs
- Understand the impact of mutations in somatic cells versus gametes
- Identify the major types of DNA mutations
Over a lifetime, our Dna can undergo changes or mutations in the sequence of bases: A, C, Grand and T. This results in changes in the proteins that are fabricated. This tin can exist a bad or a good thing.
A mutation is a modify that occurs in our Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence, either due to mistakes when the Dna is copied or as the result of environmental factors such equally UV light and cigarette smoke. Mutations can occur during DNA replication if errors are fabricated and not corrected in time. Mutations can also occur as the event of exposure to environmental factors such as smoking, sunlight and radiations. Oft cells can recognize any potentially mutation-causing harm and repair it before it becomes a fixed mutation.
Mutations contribute to genetic variation within species. Mutations can also be inherited, particularly if they accept a positive consequence. For example, the disorder sickle cell anaemia is caused by a mutation in the gene that instructs the building of a poly peptide called hemoglobin. This causes the red blood cells to become an abnormal, rigid, sickle shape. Yet, in African populations, having this mutation also protects against malaria.
However, mutation can likewise disrupt normal gene action and crusade diseases, like cancer. Cancer is the most mutual man genetic disease; it is acquired by mutations occurring in a number of growth-controlling genes. Sometimes faulty, cancer-causing genes can exist from birth, increasing a person'southward chance of getting cancer.
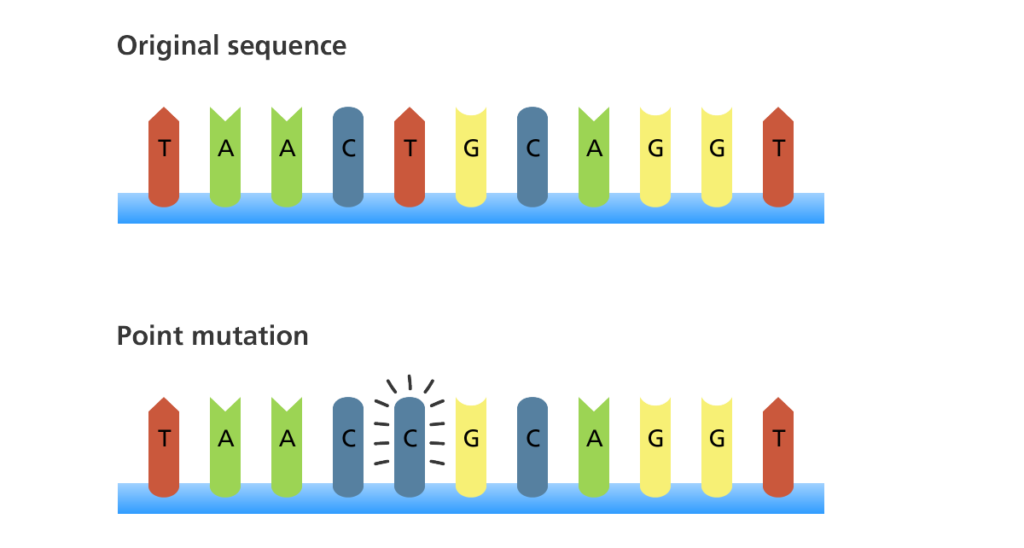
Figure one. An illustration to show an case of a DNA mutation. Image credit: Genome Research Express
Mutations in Somatic Cells and in Gametes
Permit's begin with a question: What is a cistron mutation and how do mutations occur?
A gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the Dna sequence that makes upward a factor, such that the sequence differs from what is establish in about people. Mutations range in size; they can bear upon anywhere from a single Dna building block (base pair) to a large segment of a chromosome that includes multiple genes.
Gene mutations can be classified in ii major means:
- Hereditary mutations are inherited from a parent and are present throughout a person'due south life in near every cell in the body. These mutations are also called germline mutations because they are nowadays in the parent's egg or sperm cells, which are as well called germ cells. When an egg and a sperm cell unite, the resulting fertilized egg cell receives DNA from both parents. If this DNA has a mutation, the child that grows from the fertilized egg will take the mutation in each of his or her cells.
- Caused (or somatic) mutations occur at some fourth dimension during a person'due south life and are present only in certain cells, not in every cell in the body. These changes can exist caused by environmental factors such equally ultraviolet radiation from the sun, or can occur if a mistake is made as DNA copies itself during cell division. Acquired mutations in somatic cells (cells other than sperm and egg cells) cannot be passed on to the side by side generation.
Genetic changes that are described as de novo (new) mutations can be either hereditary or somatic. In some cases, the mutation occurs in a person's egg or sperm cell just is not present in whatsoever of the person'south other cells. In other cases, the mutation occurs in the fertilized egg shortly subsequently the egg and sperm cells unite. (It is often impossible to tell exactly when a de novo mutation happened.) Every bit the fertilized egg divides, each resulting cell in the growing embryo volition have the mutation. De novo mutations may explain genetic disorders in which an affected kid has a mutation in every cell in the body but the parents exercise not, and at that place is no family history of the disorder.
Somatic mutations that happen in a single cell early in embryonic development tin can atomic number 82 to a state of affairs called mosaicism. These genetic changes are not present in a parent's egg or sperm cells, or in the fertilized egg, simply happen a chip subsequently when the embryo includes several cells. Every bit all the cells divide during growth and evolution, cells that arise from the cell with the altered gene volition take the mutation, while other cells volition not. Depending on the mutation and how many cells are afflicted, mosaicism may or may not cause health problems.
Nearly illness-causing cistron mutations are uncommon in the general population. All the same, other genetic changes occur more frequently. Genetic alterations that occur in more than than 1 percent of the population are called polymorphisms. They are common enough to be considered a normal variation in the DNA. Polymorphisms are responsible for many of the normal differences betwixt people such as middle color, pilus colour, and blood type. Although many polymorphisms take no negative effects on a person's wellness, some of these variations may influence the hazard of developing certain disorders.
Major Types of Mutations

Figure two. Xeroderma pigmentosa is a condition in which thymine dimerization from exposure to UV is not repaired. Exposure to sunlight results in skin lesions. (credit: James Halpern et al.)
A well-studied case of a mutation is seen in people suffering from xeroderma pigmentosa (Figure 2). Affected individuals have peel that is highly sensitive to UV rays from the sun.
When individuals are exposed to UV, pyrimidine dimers, especially those of thymine, are formed; people with xeroderma pigmentosa are not able to repair the harm. These are not repaired because of a defect in the nucleotide excision repair enzymes, whereas in normal individuals, the thymine dimers are excised and the defect is corrected. The thymine dimers distort the construction of the DNA double helix, and this may cause bug during Dna replication. People with xeroderma pigmentosa may have a higher risk of contracting skin cancer than those who don't take the status.
Errors during Deoxyribonucleic acid replication are not the only reason why mutations arise in Deoxyribonucleic acid.Mutations, variations in the nucleotide sequence of a genome, tin also occur because of damage to DNA. Such mutations may exist of two types: induced or spontaneous. Induced mutations are those that issue from an exposure to chemicals, UV rays, x-rays, or some other environmental amanuensis. Spontaneous mutations occur without any exposure to any environmental agent; they are a upshot of natural reactions taking place within the body.
Mutations may take a wide range of effects. Some mutations are not expressed; these are known equallysilent mutations. Point mutations are those mutations that touch on a single base of operations pair. The most common nucleotide mutations are substitutions, in which 1 base is replaced past another. These tin can be of two types, either transitions or transversions. Transition substitution refers to a purine or pyrimidine being replaced by a base of the same kind; for case, a purine such as adenine may exist replaced by the purine guanine. Transversion substitution refers to a purine being replaced past a pyrimidine, or vice versa; for example, cytosine, a pyrimidine, is replaced by adenine, a purine. Mutations can also be the consequence of the improver of a base, known as an insertion, or the removal of a base, besides known every bit deletion. Sometimes a slice of Deoxyribonucleic acid from ane chromosome may get moved to some other chromosome or to another region of the same chromosome; this is also known as translocation.
Mutations in repair genes have been known to cause cancer. Many mutated repair genes have been implicated in certain forms of pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, and colorectal cancer. Mutations tin affect either somatic cells or germ cells. If many mutations accumulate in a somatic prison cell, they may lead to problems such every bit the uncontrolled prison cell sectionalisation observed in cancer. If a mutation takes place in germ cells, the mutation will be passed on to the next generation, equally in the case of hemophilia and xeroderma pigmentosa.
The Causes of Genetic Mutations
In Summary: Deoxyribonucleic acid Mutations
Dna polymerase can brand mistakes while adding nucleotides. Almost mistakes are corrected, but if they are not, they may outcome in a mutation defined every bit a permanent alter in the Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence. Mutations can be of many types, such as exchange, deletion, insertion, and translocation. Mutations in repair genes may lead to serious consequences such every bit cancer. Mutations can exist induced or may occur spontaneously.
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to run across how well you empathise the topics covered in the previous section. This short quiz doesnot count toward your course in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and make up one's mind whether to (1) report the previous section farther or (two) move on to the next section.
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopen-biology1/chapter/dna-mutations/
Posted by: outlawdocke1945.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What If A Mutation Occurred In The Human Insulin Gene And The First Triplet Was Changed To Ccg"
Post a Comment